Implementing YOLOV1 from scratch using Keras Tensorflow 2.0
Checkout mdedit.ai, AI powered Markdown Editor for tech writers
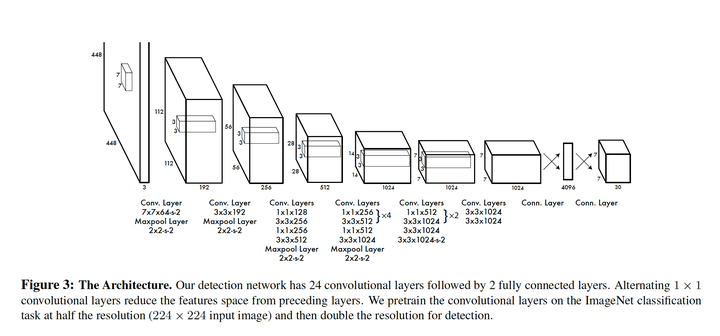
In this notebook I am going to implement YOLOV1 as described in the paper You Only Look Once. The goal is to replicate the model as described in the paper and in the process, understand the nuances of using Keras on a complex problem.
| import tensorflow as tf | |
| import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # for plotting the images | |
| %matplotlib inline |
Data Preprocessing
I would be using VOC 2007 dataset as its size is manageable so it would be easy to run it using Google Colab.
First, I download and extract the dataset.
| !wget http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/voc2007/VOCtrainval_06-Nov-2007.tar | |
| !wget http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/voc2007/VOCtest_06-Nov-2007.tar | |
| !tar xvf VOCtrainval_06-Nov-2007.tar | |
| !tar xvf VOCtest_06-Nov-2007.tar | |
| !rm VOCtrainval_06-Nov-2007.tar | |
| !rm VOCtest_06-Nov-2007.tar |
Next, we process the annotations and write the labels in a text file. A text file is easier to consume as compared to XML.
| import argparse | |
| import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET | |
| import os | |
| parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Build Annotations.') | |
| parser.add_argument('dir', default='..', help='Annotations.') | |
| sets = [('2007', 'train'), ('2007', 'val'), ('2007', 'test')] | |
| classes_num = {'aeroplane': 0, 'bicycle': 1, 'bird': 2, 'boat': 3, 'bottle': 4, 'bus': 5, | |
| 'car': 6, 'cat': 7, 'chair': 8, 'cow': 9, 'diningtable': 10, 'dog': 11, | |
| 'horse': 12, 'motorbike': 13, 'person': 14, 'pottedplant': 15, 'sheep': 16, | |
| 'sofa': 17, 'train': 18, 'tvmonitor': 19} | |
| def convert_annotation(year, image_id, f): | |
| in_file = os.path.join('VOCdevkit/VOC%s/Annotations/%s.xml' % (year, image_id)) | |
| tree = ET.parse(in_file) | |
| root = tree.getroot() | |
| for obj in root.iter('object'): | |
| difficult = obj.find('difficult').text | |
| cls = obj.find('name').text | |
| classes = list(classes_num.keys()) | |
| if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1: | |
| continue | |
| cls_id = classes.index(cls) | |
| xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox') | |
| b = (int(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), int(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), | |
| int(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), int(xmlbox.find('ymax').text)) | |
| f.write(' ' + ','.join([str(a) for a in b]) + ',' + str(cls_id)) |
| for year, image_set in sets: | |
| print(year, image_set) | |
| with open(os.path.join('VOCdevkit/VOC%s/ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (year, image_set)), 'r') as f: | |
| image_ids = f.read().strip().split() | |
| with open(os.path.join("VOCdevkit", '%s_%s.txt' % (year, image_set)), 'w') as f: | |
| for image_id in image_ids: | |
| f.write('%s/VOC%s/JPEGImages/%s.jpg' % ("VOCdevkit", year, image_id)) | |
| convert_annotation(year, image_id, f) | |
| f.write('\n') |
2007 train
2007 val
2007 test
Next, I am adding a function to prepare the input and the output. The input is a (448, 448, 3) image and the output is a (7, 7, 30) tensor. The output is based on S x S x (B * 5 +C).
S X S is the number of grids B is the number of bounding boxes per grid C is the number of predictions per grid
| import cv2 as cv | |
| import numpy as np | |
| def read(image_path, label): | |
| image = cv.imread(image_path) | |
| image = cv.cvtColor(image, cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB) | |
| image_h, image_w = image.shape[0:2] | |
| image = cv.resize(image, (448, 448)) | |
| image = image / 255. | |
| label_matrix = np.zeros([7, 7, 30]) | |
| for l in label: | |
| l = l.split(',') | |
| l = np.array(l, dtype=np.int) | |
| xmin = l[0] | |
| ymin = l[1] | |
| xmax = l[2] | |
| ymax = l[3] | |
| cls = l[4] | |
| x = (xmin + xmax) / 2 / image_w | |
| y = (ymin + ymax) / 2 / image_h | |
| w = (xmax - xmin) / image_w | |
| h = (ymax - ymin) / image_h | |
| loc = [7 * x, 7 * y] | |
| loc_i = int(loc[1]) | |
| loc_j = int(loc[0]) | |
| y = loc[1] - loc_i | |
| x = loc[0] - loc_j | |
| if label_matrix[loc_i, loc_j, 24] == 0: | |
| label_matrix[loc_i, loc_j, cls] = 1 | |
| label_matrix[loc_i, loc_j, 20:24] = [x, y, w, h] | |
| label_matrix[loc_i, loc_j, 24] = 1 # response | |
| return image, label_matrix |
Training the model
Next, I am defining a custom generator that returns a batch of input and outputs.
| from tensorflow import keras | |
| class My_Custom_Generator(keras.utils.Sequence) : | |
| def __init__(self, images, labels, batch_size) : | |
| self.images = images | |
| self.labels = labels | |
| self.batch_size = batch_size | |
| def __len__(self) : | |
| return (np.ceil(len(self.images) / float(self.batch_size))).astype(np.int) | |
| def __getitem__(self, idx) : | |
| batch_x = self.images[idx * self.batch_size : (idx+1) * self.batch_size] | |
| batch_y = self.labels[idx * self.batch_size : (idx+1) * self.batch_size] | |
| train_image = [] | |
| train_label = [] | |
| for i in range(0, len(batch_x)): | |
| img_path = batch_x[i] | |
| label = batch_y[i] | |
| image, label_matrix = read(img_path, label) | |
| train_image.append(image) | |
| train_label.append(label_matrix) | |
| return np.array(train_image), np.array(train_label) |
The code snippet below, prepares arrays with inputs and outputs.
| train_datasets = [] | |
| val_datasets = [] | |
| with open(os.path.join("VOCdevkit", '2007_train.txt'), 'r') as f: | |
| train_datasets = train_datasets + f.readlines() | |
| with open(os.path.join("VOCdevkit", '2007_val.txt'), 'r') as f: | |
| val_datasets = val_datasets + f.readlines() | |
| X_train = [] | |
| Y_train = [] | |
| X_val = [] | |
| Y_val = [] | |
| for item in train_datasets: | |
| item = item.replace("\n", "").split(" ") | |
| X_train.append(item[0]) | |
| arr = [] | |
| for i in range(1, len(item)): | |
| arr.append(item[i]) | |
| Y_train.append(arr) | |
| for item in val_datasets: | |
| item = item.replace("\n", "").split(" ") | |
| X_val.append(item[0]) | |
| arr = [] | |
| for i in range(1, len(item)): | |
| arr.append(item[i]) | |
| Y_val.append(arr) |
Next, we create instances of the generator for our training and validation sets.
| batch_size = 4 | |
| my_training_batch_generator = My_Custom_Generator(X_train, Y_train, batch_size) | |
| my_validation_batch_generator = My_Custom_Generator(X_val, Y_val, batch_size) | |
| x_train, y_train = my_training_batch_generator.__getitem__(0) | |
| x_val, y_val = my_training_batch_generator.__getitem__(0) | |
| print(x_train.shape) | |
| print(y_train.shape) | |
| print(x_val.shape) | |
| print(y_val.shape) |
(4, 448, 448, 3)
(4, 7, 7, 30)
(4, 448, 448, 3)
(4, 7, 7, 30)
Define a custom output layer
We need to reshape the output from the model so we define a custom Keras layer for it.
| from tensorflow import keras | |
| import keras.backend as K | |
| class Yolo_Reshape(tf.keras.layers.Layer): | |
| def __init__(self, target_shape): | |
| super(Yolo_Reshape, self).__init__() | |
| self.target_shape = tuple(target_shape) | |
| def get_config(self): | |
| config = super().get_config().copy() | |
| config.update({ | |
| 'target_shape': self.target_shape | |
| }) | |
| return config | |
| def call(self, input): | |
| # grids 7x7 | |
| S = [self.target_shape[0], self.target_shape[1]] | |
| # classes | |
| C = 20 | |
| # no of bounding boxes per grid | |
| B = 2 | |
| idx1 = S[0] * S[1] * C | |
| idx2 = idx1 + S[0] * S[1] * B | |
| # class probabilities | |
| class_probs = K.reshape(input[:, :idx1], (K.shape(input)[0],) + tuple([S[0], S[1], C])) | |
| class_probs = K.softmax(class_probs) | |
| #confidence | |
| confs = K.reshape(input[:, idx1:idx2], (K.shape(input)[0],) + tuple([S[0], S[1], B])) | |
| confs = K.sigmoid(confs) | |
| # boxes | |
| boxes = K.reshape(input[:, idx2:], (K.shape(input)[0],) + tuple([S[0], S[1], B * 4])) | |
| boxes = K.sigmoid(boxes) | |
| outputs = K.concatenate([class_probs, confs, boxes]) | |
| return outputs |
Defining the YOLO model.
Next, we define the model as described in the original paper.
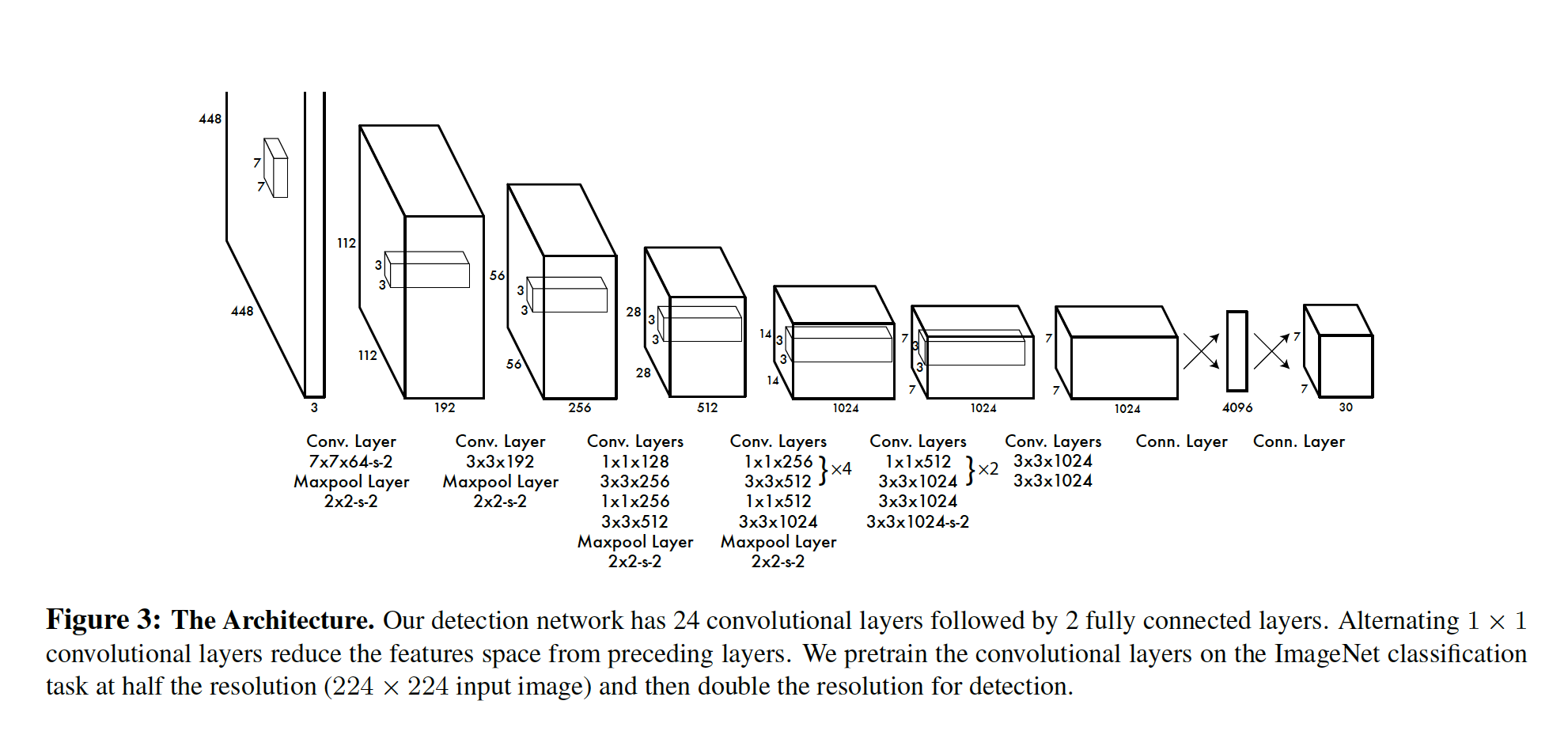
| from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential | |
| from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, InputLayer, Dropout, Flatten, Reshape | |
| from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, GlobalMaxPooling2D | |
| from tensorflow.keras.regularizers import l2 | |
| lrelu = tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU(alpha=0.1) | |
| nb_boxes=1 | |
| grid_w=7 | |
| grid_h=7 | |
| cell_w=64 | |
| cell_h=64 | |
| img_w=grid_w*cell_w | |
| img_h=grid_h*cell_h | |
| model = Sequential() | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size= (7, 7), strides=(1, 1), input_shape =(img_h, img_w, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2), padding = 'same')) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=192, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2), padding = 'same')) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size= (1, 1), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size= (1, 1), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2), padding = 'same')) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size= (1, 1), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size= (1, 1), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size= (1, 1), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=256, kernel_size= (1, 1), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size= (1, 1), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=1024, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2), padding = 'same')) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size= (1, 1), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=1024, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=512, kernel_size= (1, 1), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=1024, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=1024, kernel_size= (3, 3), padding = 'same', activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=1024, kernel_size= (3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding = 'same')) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=1024, kernel_size= (3, 3), activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Conv2D(filters=1024, kernel_size= (3, 3), activation=lrelu, kernel_regularizer=l2(5e-4))) | |
| model.add(Flatten()) | |
| model.add(Dense(512)) | |
| model.add(Dense(1024)) | |
| model.add(Dropout(0.5)) | |
| model.add(Dense(1470, activation='sigmoid')) | |
| model.add(Yolo_Reshape(target_shape=(7,7,30))) | |
| model.summary() | |
| Here's the model summary. | |
Model: "sequential_5"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d_120 (Conv2D) (None, 448, 448, 64) 9472
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_20 (MaxPooling (None, 224, 224, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_121 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 192) 110784
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_21 (MaxPooling (None, 112, 112, 192) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_122 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 24704
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_123 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 256) 295168
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_124 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 256) 65792
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_125 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 512) 1180160
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_22 (MaxPooling (None, 56, 56, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_126 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 131328
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_127 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 512) 1180160
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_128 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 131328
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_129 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 512) 1180160
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_130 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 131328
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_131 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 512) 1180160
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_132 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 131328
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_133 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 512) 1180160
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_134 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 512) 262656
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_135 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 1024) 4719616
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_23 (MaxPooling (None, 28, 28, 1024) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_136 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 524800
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_137 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 1024) 4719616
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_138 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 524800
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_139 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 1024) 4719616
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_140 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 1024) 9438208
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_141 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 1024) 9438208
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_142 (Conv2D) (None, 12, 12, 1024) 9438208
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_143 (Conv2D) (None, 10, 10, 1024) 9438208
_________________________________________________________________
flatten_5 (Flatten) (None, 102400) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_15 (Dense) (None, 512) 52429312
_________________________________________________________________
dense_16 (Dense) (None, 1024) 525312
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_5 (Dropout) (None, 1024) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_17 (Dense) (None, 1470) 1506750
_________________________________________________________________
yolo__reshape_10 (Yolo_Resha (None, 7, 7, 30) 0
=================================================================
Total params: 114,617,342
Trainable params: 114,617,342
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
Define a custom learning rate scheduler
The paper uses different learning rates for different epochs. So we define a custom Callback function for the learning rate.
| from tensorflow import keras | |
| class CustomLearningRateScheduler(keras.callbacks.Callback): | |
| """Learning rate scheduler which sets the learning rate according to schedule. | |
| Arguments: | |
| schedule: a function that takes an epoch index | |
| (integer, indexed from 0) and current learning rate | |
| as inputs and returns a new learning rate as output (float). | |
| """ | |
| def __init__(self, schedule): | |
| super(CustomLearningRateScheduler, self).__init__() | |
| self.schedule = schedule | |
| def on_epoch_begin(self, epoch, logs=None): | |
| if not hasattr(self.model.optimizer, "lr"): | |
| raise ValueError('Optimizer must have a "lr" attribute.') | |
| # Get the current learning rate from model's optimizer. | |
| lr = float(tf.keras.backend.get_value(self.model.optimizer.learning_rate)) | |
| # Call schedule function to get the scheduled learning rate. | |
| scheduled_lr = self.schedule(epoch, lr) | |
| # Set the value back to the optimizer before this epoch starts | |
| tf.keras.backend.set_value(self.model.optimizer.lr, scheduled_lr) | |
| print("\nEpoch %05d: Learning rate is %6.4f." % (epoch, scheduled_lr)) | |
| LR_SCHEDULE = [ | |
| # (epoch to start, learning rate) tuples | |
| (0, 0.01), | |
| (75, 0.001), | |
| (105, 0.0001), | |
| ] | |
| def lr_schedule(epoch, lr): | |
| """Helper function to retrieve the scheduled learning rate based on epoch.""" | |
| if epoch < LR_SCHEDULE[0][0] or epoch > LR_SCHEDULE[-1][0]: | |
| return lr | |
| for i in range(len(LR_SCHEDULE)): | |
| if epoch == LR_SCHEDULE[i][0]: | |
| return LR_SCHEDULE[i][1] | |
| return lr |
Define the loss function
Next, we would be defining a custom loss function to be used in the model. Take a look at this blog post to understand more about the loss function used in YOLO.
I understood the loss function but didn’t implement it on my own. I took the implementation as it is from this Github repo.
| import keras.backend as K | |
| def xywh2minmax(xy, wh): | |
| xy_min = xy - wh / 2 | |
| xy_max = xy + wh / 2 | |
| return xy_min, xy_max | |
| def iou(pred_mins, pred_maxes, true_mins, true_maxes): | |
| intersect_mins = K.maximum(pred_mins, true_mins) | |
| intersect_maxes = K.minimum(pred_maxes, true_maxes) | |
| intersect_wh = K.maximum(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, 0.) | |
| intersect_areas = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1] | |
| pred_wh = pred_maxes - pred_mins | |
| true_wh = true_maxes - true_mins | |
| pred_areas = pred_wh[..., 0] * pred_wh[..., 1] | |
| true_areas = true_wh[..., 0] * true_wh[..., 1] | |
| union_areas = pred_areas + true_areas - intersect_areas | |
| iou_scores = intersect_areas / union_areas | |
| return iou_scores | |
| def yolo_head(feats): | |
| # Dynamic implementation of conv dims for fully convolutional model. | |
| conv_dims = K.shape(feats)[1:3] # assuming channels last | |
| # In YOLO the height index is the inner most iteration. | |
| conv_height_index = K.arange(0, stop=conv_dims[0]) | |
| conv_width_index = K.arange(0, stop=conv_dims[1]) | |
| conv_height_index = K.tile(conv_height_index, [conv_dims[1]]) | |
| # TODO: Repeat_elements and tf.split doesn't support dynamic splits. | |
| # conv_width_index = K.repeat_elements(conv_width_index, conv_dims[1], axis=0) | |
| conv_width_index = K.tile( | |
| K.expand_dims(conv_width_index, 0), [conv_dims[0], 1]) | |
| conv_width_index = K.flatten(K.transpose(conv_width_index)) | |
| conv_index = K.transpose(K.stack([conv_height_index, conv_width_index])) | |
| conv_index = K.reshape(conv_index, [1, conv_dims[0], conv_dims[1], 1, 2]) | |
| conv_index = K.cast(conv_index, K.dtype(feats)) | |
| conv_dims = K.cast(K.reshape(conv_dims, [1, 1, 1, 1, 2]), K.dtype(feats)) | |
| box_xy = (feats[..., :2] + conv_index) / conv_dims * 448 | |
| box_wh = feats[..., 2:4] * 448 | |
| return box_xy, box_wh | |
| def yolo_loss(y_true, y_pred): | |
| label_class = y_true[..., :20] # ? * 7 * 7 * 20 | |
| label_box = y_true[..., 20:24] # ? * 7 * 7 * 4 | |
| response_mask = y_true[..., 24] # ? * 7 * 7 | |
| response_mask = K.expand_dims(response_mask) # ? * 7 * 7 * 1 | |
| predict_class = y_pred[..., :20] # ? * 7 * 7 * 20 | |
| predict_trust = y_pred[..., 20:22] # ? * 7 * 7 * 2 | |
| predict_box = y_pred[..., 22:] # ? * 7 * 7 * 8 | |
| _label_box = K.reshape(label_box, [-1, 7, 7, 1, 4]) | |
| _predict_box = K.reshape(predict_box, [-1, 7, 7, 2, 4]) | |
| label_xy, label_wh = yolo_head(_label_box) # ? * 7 * 7 * 1 * 2, ? * 7 * 7 * 1 * 2 | |
| label_xy = K.expand_dims(label_xy, 3) # ? * 7 * 7 * 1 * 1 * 2 | |
| label_wh = K.expand_dims(label_wh, 3) # ? * 7 * 7 * 1 * 1 * 2 | |
| label_xy_min, label_xy_max = xywh2minmax(label_xy, label_wh) # ? * 7 * 7 * 1 * 1 * 2, ? * 7 * 7 * 1 * 1 * 2 | |
| predict_xy, predict_wh = yolo_head(_predict_box) # ? * 7 * 7 * 2 * 2, ? * 7 * 7 * 2 * 2 | |
| predict_xy = K.expand_dims(predict_xy, 4) # ? * 7 * 7 * 2 * 1 * 2 | |
| predict_wh = K.expand_dims(predict_wh, 4) # ? * 7 * 7 * 2 * 1 * 2 | |
| predict_xy_min, predict_xy_max = xywh2minmax(predict_xy, predict_wh) # ? * 7 * 7 * 2 * 1 * 2, ? * 7 * 7 * 2 * 1 * 2 | |
| iou_scores = iou(predict_xy_min, predict_xy_max, label_xy_min, label_xy_max) # ? * 7 * 7 * 2 * 1 | |
| best_ious = K.max(iou_scores, axis=4) # ? * 7 * 7 * 2 | |
| best_box = K.max(best_ious, axis=3, keepdims=True) # ? * 7 * 7 * 1 | |
| box_mask = K.cast(best_ious >= best_box, K.dtype(best_ious)) # ? * 7 * 7 * 2 | |
| no_object_loss = 0.5 * (1 - box_mask * response_mask) * K.square(0 - predict_trust) | |
| object_loss = box_mask * response_mask * K.square(1 - predict_trust) | |
| confidence_loss = no_object_loss + object_loss | |
| confidence_loss = K.sum(confidence_loss) | |
| class_loss = response_mask * K.square(label_class - predict_class) | |
| class_loss = K.sum(class_loss) | |
| _label_box = K.reshape(label_box, [-1, 7, 7, 1, 4]) | |
| _predict_box = K.reshape(predict_box, [-1, 7, 7, 2, 4]) | |
| label_xy, label_wh = yolo_head(_label_box) # ? * 7 * 7 * 1 * 2, ? * 7 * 7 * 1 * 2 | |
| predict_xy, predict_wh = yolo_head(_predict_box) # ? * 7 * 7 * 2 * 2, ? * 7 * 7 * 2 * 2 | |
| box_mask = K.expand_dims(box_mask) | |
| response_mask = K.expand_dims(response_mask) | |
| box_loss = 5 * box_mask * response_mask * K.square((label_xy - predict_xy) / 448) | |
| box_loss += 5 * box_mask * response_mask * K.square((K.sqrt(label_wh) - K.sqrt(predict_wh)) / 448) | |
| box_loss = K.sum(box_loss) | |
| loss = confidence_loss + class_loss + box_loss | |
| return loss |
Add a callback for saving the weights
Next, I define a callback to keep saving the best weights.
| # defining a function to save the weights of best model | |
| from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint | |
| mcp_save = ModelCheckpoint('weight.hdf5', save_best_only=True, monitor='val_loss', mode='min') |
Compile the model
Finally, I compile the model using the custom loss function that was defined above.
| from tensorflow import keras | |
| model.compile(loss=yolo_loss ,optimizer='adam') |
Train the model
Now that we have everything setup, we will call model.fit to train the model for 135 epochs.
| model.fit(x=my_training_batch_generator, | |
| steps_per_epoch = int(len(X_train) // batch_size), | |
| epochs = 135, | |
| verbose = 1, | |
| workers= 4, | |
| validation_data = my_validation_batch_generator, | |
| validation_steps = int(len(X_val) // batch_size), | |
| callbacks=[ | |
| CustomLearningRateScheduler(lr_schedule), | |
| mcp_save | |
| ]) |
Epoch 00000: Learning rate is 0.0100.
Epoch 1/135
625/625 [==============================] - 195s 311ms/step - loss: 88.0331 - val_loss: 245.3397
Epoch 00001: Learning rate is 0.0100.
Epoch 2/135
625/625 [==============================] - 194s 310ms/step - loss: 140.9500 - val_loss: 116.6240
Epoch 00002: Learning rate is 0.0100.
Epoch 3/135
625/625 [==============================] - 194s 310ms/step - loss: 114.1760 - val_loss: 113.2524
Epoch 00003: Learning rate is 0.0100.
Epoch 4/135
625/625 [==============================] - 194s 310ms/step - loss: 113.0043 - val_loss: 112.8592
Epoch 00004: Learning rate is 0.0100.
Epoch 5/135
625/625 [==============================] - 189s 303ms/step - loss: 112.9847 - val_loss: 113.3475
Epoch 00005: Learning rate is 0.0100.
Epoch 6/135
625/625 [==============================] - 194s 310ms/step - loss: 113.0094 - val_loss: 112.7520
Epoch 00006: Learning rate is 0.0100.
Epoch 7/135
625/625 [==============================] - 194s 310ms/step - loss: 71.0617 - val_loss: 61.3470
Conclusion
It was a good exercise to implement YOLO V1 from scratch and understand various nuances of writing a model from scratch. This implementation won’t achieve the same accuracy as what was described in the paper since we have skipped the pretraining step.
